Table of Contents
Delivery Pain Points
1. Suboptimal route
The logistics department has to deliver 1000 orders with 30 vehicles to 800 different locations per day. How should they arrange the delivery route so that the distance traveled is as optimal as possible? How to divide it and assign it to each driver of the vehicle?
Routes from a manual planning process are usually less than optimal, or have been optimal but took a long time to process and require a lot of resources.
2. Vehicle Capacity
In addition to assigning drivers, companies must also remember the capacity of each vehicle they own (or rent). This capacity varies greatly depending on the specifications, both in terms of volume and maximum weight of goods that can be transported. If vehicle utilization is low, it will increase transportation costs, starting from fuels, drivers and vehicle rental prices.
Even with the most experienced route planning supervisor, this process cannot be solved manually because there are so many other factors to consider. Maximizing the route with the vehicle capacity requires a great deal of effort in computerizing the planning process.
3. Operational Constraints
Route planning is not only about making the fastest and shortest routes, during the actual implementation in the field, there are many other factors that contribute for the company to have the most optimal route planning. Examples include driver working hours and working days, vehicle availability status, road regulations (especially vehicle type and maximum weight), to the handling type of each product (for example, must be stored in a refrigerated machine or a fast expiration date).
5. Limited Operating Hours
With warehouse opening hours or store business hours, companies are expected to fulfill delivery orders on predetermined days and hours with the least amount of time. By considering operational hours limits, waiting time for drivers for loading/unloading of goods can be optimized.
6. Last Minute Product Orders
Shipping goods is one of those businesses that must always facilitate change. Prioritized customers sometimes order, cancel or reschedule delivery of orders suddenly. This causes an interference with the delivery schedule that has been planned in advance. However, if this demand is not adapted quickly it can result in lost time, profit, and customer satisfaction.
7. System That Can Learn Real Variables From the Field
Delivery process involves many complex documents. If this proof of delivery is only collected without further analysis, the company will not be able to find out what routes and shipping methods are the most optimal for their distribution network, warehouse locations and which operators are the most suitable to the customer base, and other shipping data needs.
8. Increased Customer Demand for the Shipping Tracking Feature
In a competitive business, the differences between companies are often subtle. That is why many companies start to offer more to improve their customer experience, for example, such as tracking delivery features for customers.
Delivery Route Planning Solutions
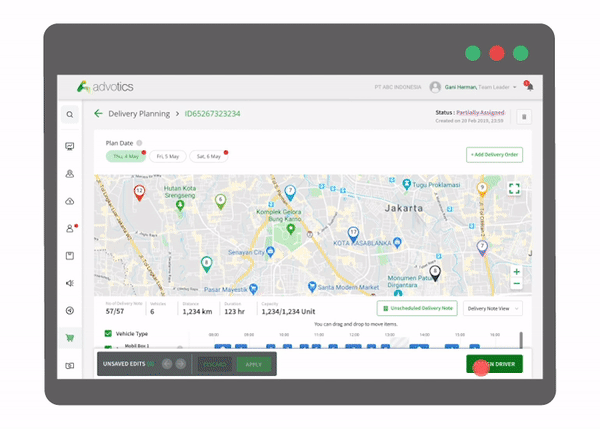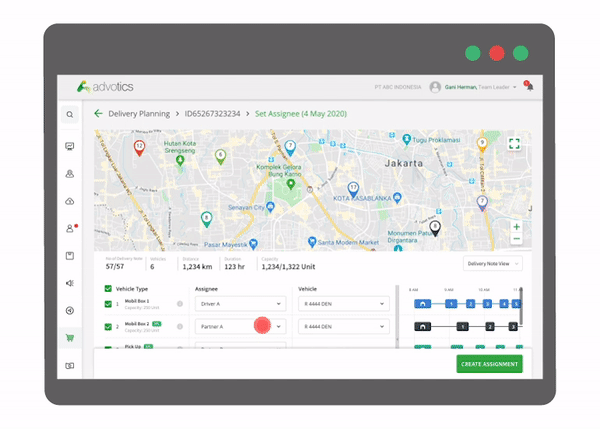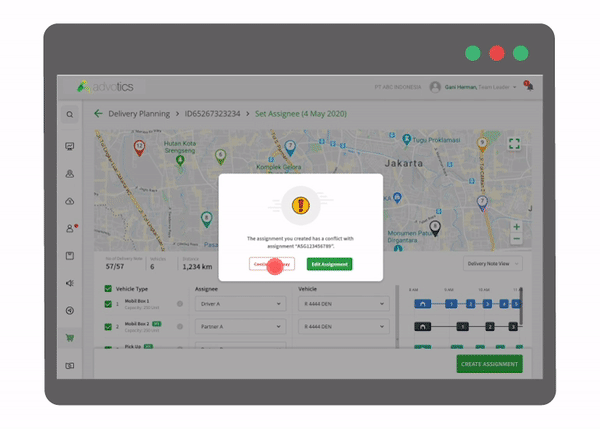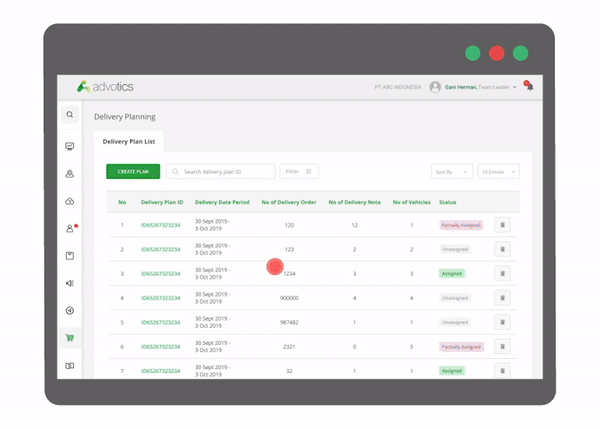
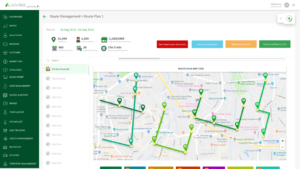
1. Route Planning and Driver/Vehicle Assignments Automation
Each shipment of goods is automatically assigned to the most optimal delivery route with the most suitable vehicle. The capacity of the vehicle is paired to the most suitable type of product so that delivery can be maximized both by weight and volume. In addition, constraints such as warehouse/store operating hours and employee working hours can also be entered in the database to be considered in route scheduling. Planning process time is improved, making it perfect for planning daily or weekly deliveries.
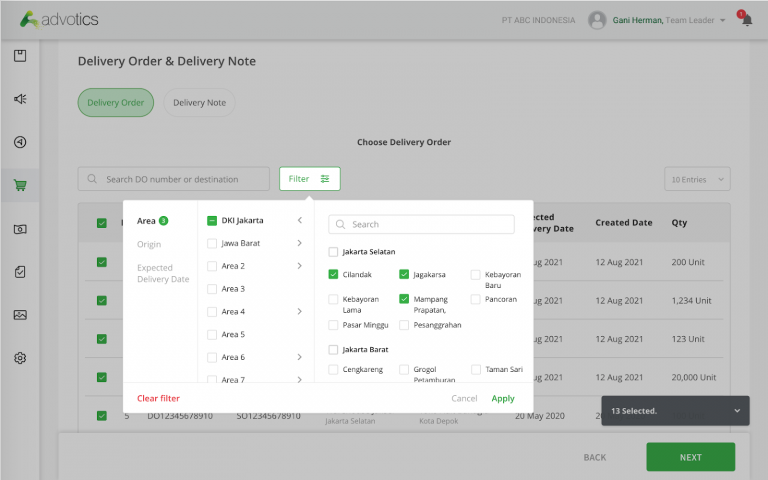
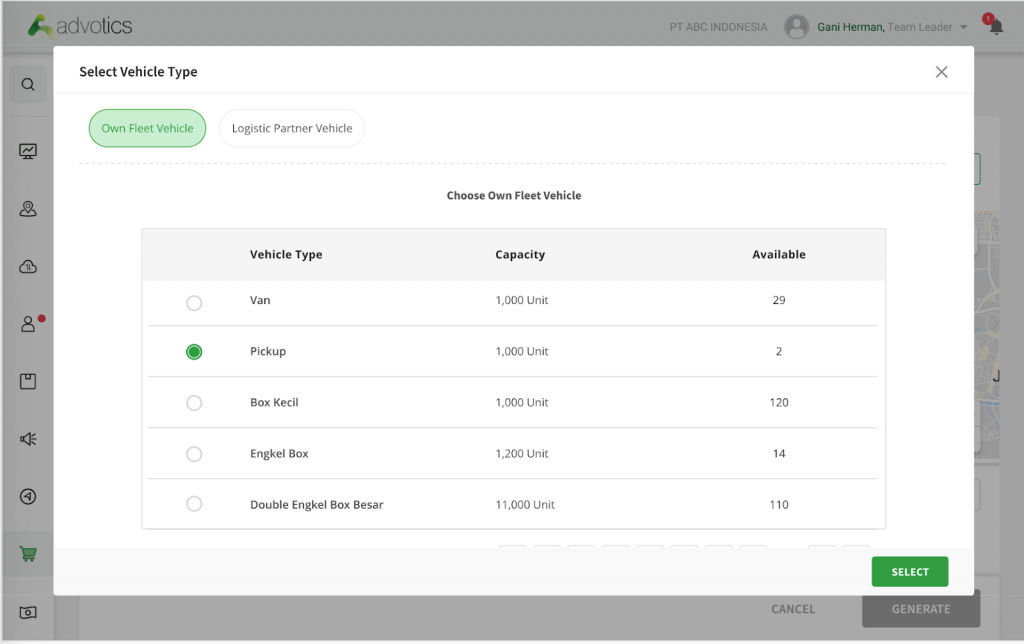
2. Manage Last-Minute Requests
Delivery Planning System (DPS) can accommodate sudden requests for goods and services, as well as anticipate schedule cancellations from customers. Dynamic scheduling and re-routing will generate more profit by reducing vehicle idle time.
3. Direct Assignment to Driver
Route assignments can be sent directly via the driver’s application. Detailed information such as vehicle plates, a list of delivery destinations to print road documents can be checked in one application.
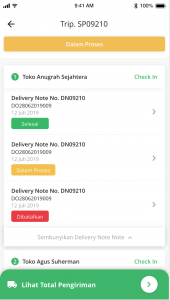
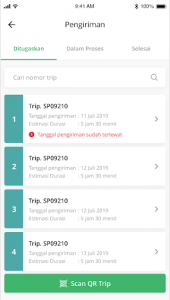
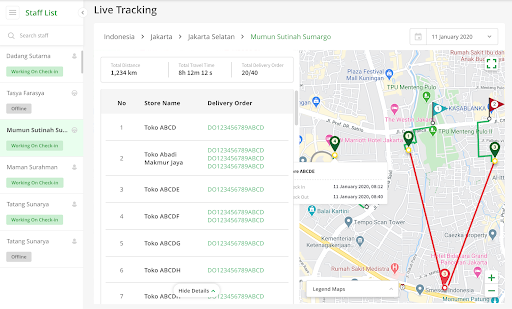
4. Inspection of Shipping Data History
All collected historical data can be downloaded for performance reports and can also be used as insights for more optimal route planning in the future. For example, have vehicles been allocated correctly? Are there still idle vehicles? Which areas are the highest in demand for delivery of goods? Should there be an increase in vehicles in anticipation of higher demand for goods?
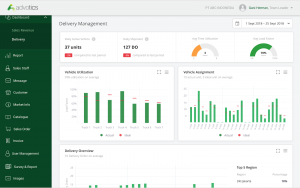
5. Evidence of Electronic Delivery
Record signatures (recipient, sender, driver, warehouse checker), product photos, and scan QR code to authenticate delivery of goods. The delivery location can also be verified as the driver must be at the location of the recipient’s coordinates to be able to complete the delivery.
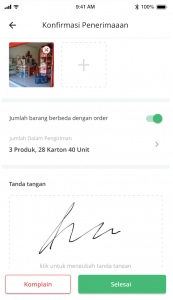
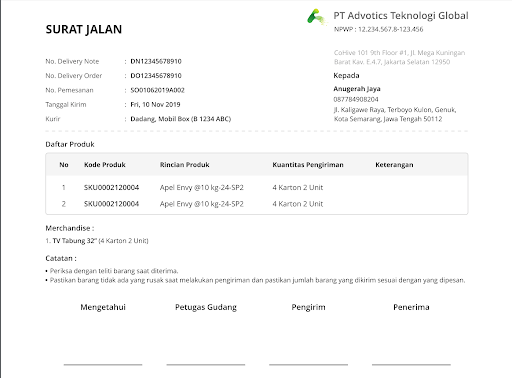
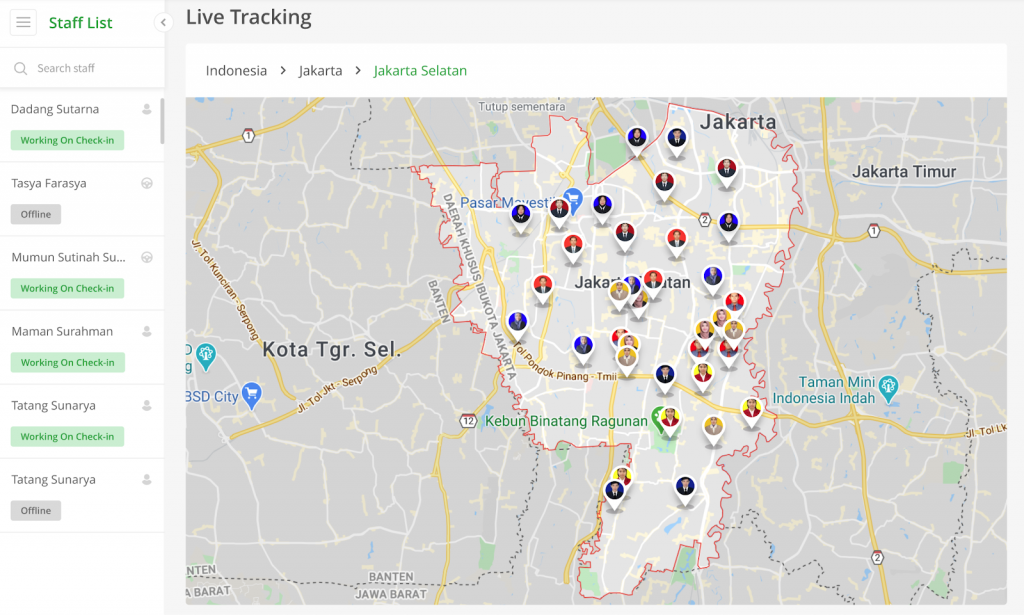
6. Live Route Tracking
From factory warehouses to stores, every driver/vehicle is equipped with a mobile app-based GPS tracker that can be seen in real-time and integrated safely and easily. Managers can remotely monitor each fleet’s ETA for unannounced rerouting.